316, Sakar 7 Near Nehrubridge Ashram road Ahmedabad


316, Sakar 7 Near Nehrubridge Ashram road Ahmedabad
Lupus is a long-term autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks normal, healthy tissues.
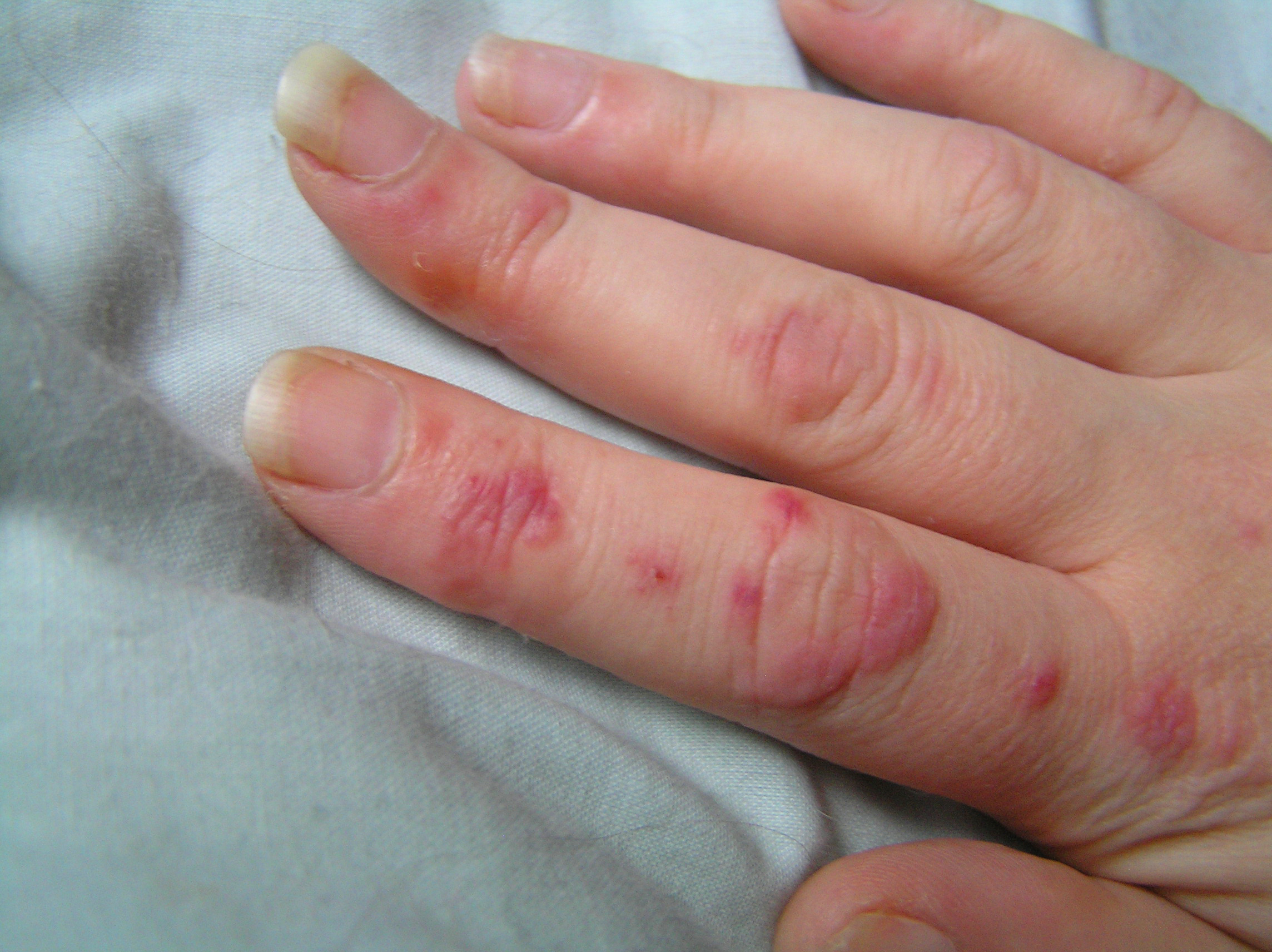
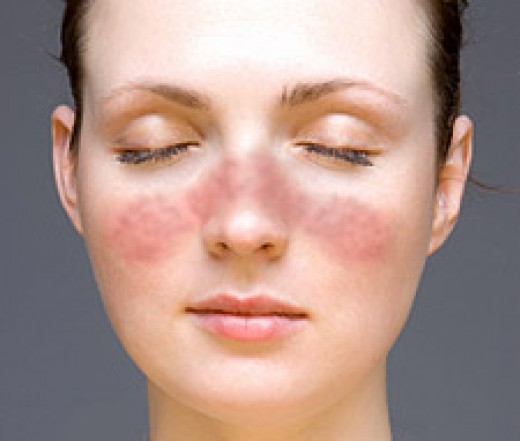
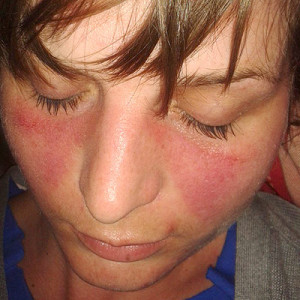
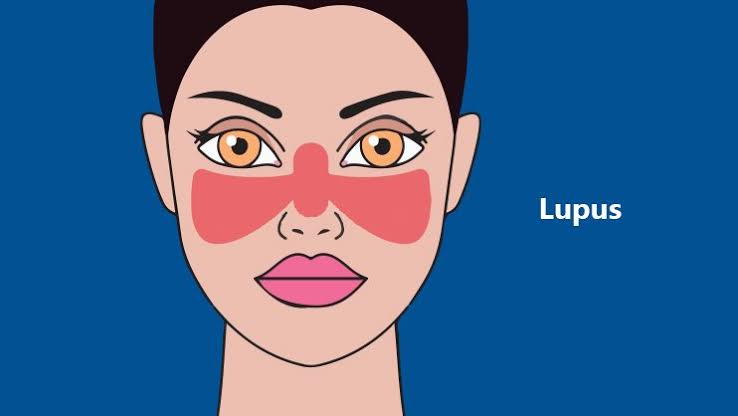
Skin problems are a common feature of lupus. Some people with lupus have a red rash over their cheeks and the bridge of their nose -- called a "butterfly" or malar rash. Hair loss and mouth sores are also common.
Arthritis is very common in people with lupus. There may be pain, with or without swelling. Stiffness and pain may be particularly evident in the morning. Arthritis may be a problem for only a few days or weeks, or may be a permanent feature of the disease.
Kidney involvement in people with lupus can be life threatening and may occur in up to half of those with lupus.
Blood involvement can occur with or without other symptoms. People with lupus may have dangerous reductions in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets (particles that help clot the blood).
Brain involvement is, fortunately, a rare problem in people with lupus. When present, it may cause confusion, depression, seizures, and, rarely, strokes. Involvement of the spinal cord (transverse myelitis) can cause numbness and weakness.
Heart and lung involvement often is caused by inflammation of the covering of the heart (pericardium) and lungs (pleura). When these structures become inflamed, patients may develop chest pain, irregular heartbeat, and accumulation of fluid around the lungs (pleuritis or pleurisy) and heart (pericarditis).
Research shows that certain genes play a role in the development of lupus. The different forms of these genes carry instructions for proteins that may affect the immune system. Researchers are studying how high levels or low levels of these proteins may be important in the development of the disease.
Exposure to certain factors in the environment – such as viral infections, sunlight, certain medications, and smoking – may trigger lupus.
Researchers think that if the body does not remove damaged or dead cells normally, this could trick the immune system into constantly fighting against itself. This process could cause an autoimmune response, which could lead to lupus. In addition, researchers are studying different cell types and how changes could lead to lupus.
Some prescription medications such as hydralazine and procainamide can cause lupus. The symptoms usually get better after you stop taking the drug.
here are a number of other things that could make you more likely to get lupus, like: Sex. 90% of people diagnosed with the disease are women. Age. Women 14 to 45 years old are most often affected. Family history. Lupus sometimes affects more than one member of a family. But only about 10% of people with lupus have a close relative with the disease.
This is the most common form of lupus, where inflammation from a faulty immune system inflames a number of organs or organ systems.
This is inflammation of the kidneys due to SLE.
Here, your faulty immune response causes skin rashes or lesions.
Medication causes this type of lupus. Symptoms may stop when medication stops.
his form of lupus happens to infants whose mothers have SLE.